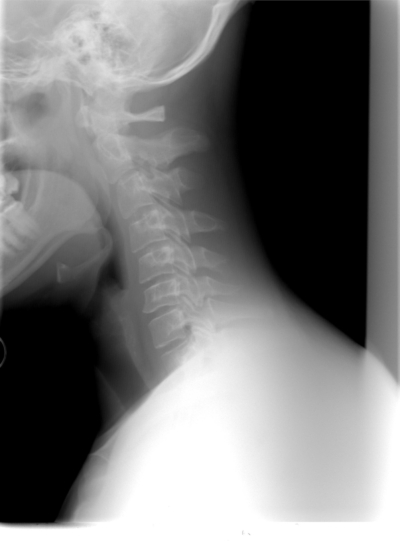
Percutaneous Fixation of Levine-Edwards Type II Hangman’s Fractures Under the Guidance of an Orthopedic Robot
Have you ever considered how orthopedic surgeons operate cervical bone fractures? Well, they usually haven’t preferred to operate these fractures. They usually suggest conservative treatment methods even if they have complications. With the development of technology, this article proposed a minimally invasive and robot-assisted technique for the treatment of Levine-Edwards type II hangman’s fractures. Postoperatively, all the fractures in this research have healed in likely 3.5 months and there was no neurovascular injury associated with this technique. This article indicates that 3D-fluoroscopy-based, robot-assisted C2 pedicle is a safe, precise, and feasible method for initial treatment of L-E type II hangman’s fractures.
Superficial Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm After Intra-articular Adductor Canal Pain Catheter Placement for Total Knee Arthroplasty
Did you know that inflammation of your joints may cause vascular injuries? Do you know the importance of suspicion in patients presenting with acute swelling in the postoperative period? Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) with vascular injury is a rare complication but in this article they present a case of superficial femoral artery aneurysm in a patient with TKA after they’ve set an intra-articular On-Q pain catheter placement into adductor canal for postoperative pain control. The researchers suggest that use of intra-articular On-Q pain catheters can be a safe technique to help manage postoperative pain following TKA. But it also may cause trauma to vessels during catheter placement and this may result in SFA aneurysm, so it will be better for you to be focused! Because if identified in a timely fashion, treatment with stenting or selective catheter embolization can successfully treat this issue and help avoid further complications.
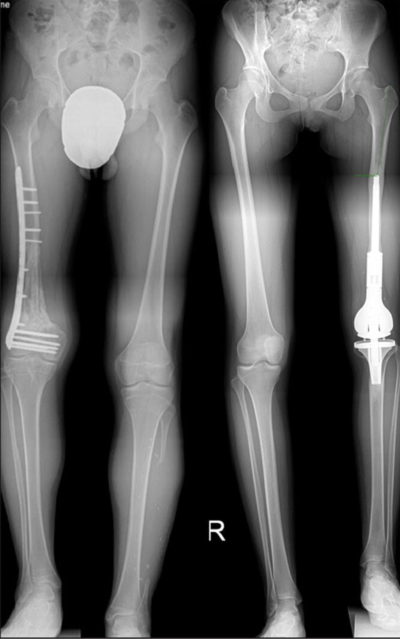
Femoral Discrepancy After Childhood Bone Sarcoma Surgery Can Be Treated With Magnetic Intramedullary Nails
Are all people lucky enough to be born completely healthy? Some children have to struggle with femoral length discrepancy caused by limb salvage in their skeletal maturation period. As the doctors of the future, we have to give them a better life which is equal to their peers and this study helps us to find a safe technique with determine that magnetic motorized intramedullary nail (PRECICE) is safe and effective in these patients. The outcomes of this study demonstrate that PRECICE implant can safely and effectively correct femoral length discrepancy caused by limb salvage performed for osteosarcoma before skeletal maturity.
Macrophages and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
Is there any possibility that your macrophages could be the reason for your disease while they are trying to save you from the disease? The intervertebral disc (IVD) disease contributes to low back pain and significant disability in many individuals. Increasing evidence suggests that IVD degeneration is a disease of the whole joint that is associated with significant inflammation. Moreover, studies show elevated macrophage accumulation within the IVD with increasing levels of disease severity; however, we still need to understand the roles, be they causative or consequential, of macrophages during the degenerative process. This study aims to discuss hallmarks of IVD degeneration and the role of macrophages in IVD degeneration.
Perspectives of Motor Functional Upper Extremity Recovery with the Use of Immersive Virtual Reality in Stroke Patients
Do you think virtual reality (VR) is worth considering as a form of physical therapy? Stroke is one of the leading causes of disability, including loss of hand manipulative skills. It is becoming more common to apply VR as physiotherapeutic methods. The aim of this study was to establish whether immersive VR was worth considering as a form of physical therapy and the advisability of applying it in restoring post-stroke hand function impairment. They indicate that applying Virtual Mirror Hand 1.0 treatment to patients after stroke appears to be at least as good as classical mirror therapy solution and definitely provides the opportunity to consider the VR application as an integral part of neurorehabilitation after stroke. They also suggest that only VR therapy patients reported improvement in pain and multiple subjective sensations. The development of the Virtual Mirror Hand 1.0 system is likely to be equivalent to increasing the quality of the treatment and delivering even greater benefits for patients.