Gut Microbiota-derived Metabolites and Their Importance in Neurological Disorders
Do you know the importance of your microbial-derived metabolites for your gut-brain axis and their potential effects on neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders?
Microbial-derived metabolites are one of the most important molecules for the gut-brain connection and they are products of bacterial digestion. Depending on their levels in the host, they can exert beneficial or detrimental effects on the brain and they may cause several neurodegenerative disorders. In this study, they have reviewed some well-known metabolites to highlight the underlying mechanisms of maintaining intestinal homeostasis and regulating neuroimmunoendocrine function.
Gut Microbiota Modulation of Efficacy and Toxicity of Cancer Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
What do you think about the effects of the microbial community residing in the gastrointestinal tract to cancer therapy?
The gut microbiota interact with anticancer drugs, potentially influencing their absorption, distribution, and metabolism. That’s why they play a significant role in the effectiveness and side effects of cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy. This study suggests that modulating this environment with pre- and probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation may have potential as a strategy to improve cancer treatment outcomes and reduce toxicity and side effects.
Gut Microbiota-Bile Acid-Skeletal Muscle Axis
Do you think your bile acid metabolism can affect your skeletal muscle health?
This article explores that dysbiosis, which is defined as low microbial diversity and an unstable composition over time, results in a substantial alteration of skeletal muscle metabolism and function through various mechanisms, such as regulating energy metabolism and muscle protein synthesis. Also, they emphasize that gut microbiota-bile acid-skeletal muscle axis may be an important target for promoting skeletal muscle health through the use of prebiotics, probiotics, or bile acid sequestrants and the importance of further research in this area for developing new therapies for muscle-related diseases.
Abnormal Proliferation of Gut Mycobiota Contributes to the Aggravation of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) and related metabolic disorders constitute a worldwide health threat, and studies of the last decade show us that gut-microbiota play a crucial role in the regulation of energy and substance metabolism, which affect the development of T2D. Changes in gut microbiota have been linked to metabolic changes that can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance. Researchers observed that the ablation of the commensal fungi in mice can protect high fat diet induced insulin resistance and related metabolic disorders. They indicate the importance of preventing gut microbiota from certain fungal species as a promising strategy to alleviate insulin resistance.
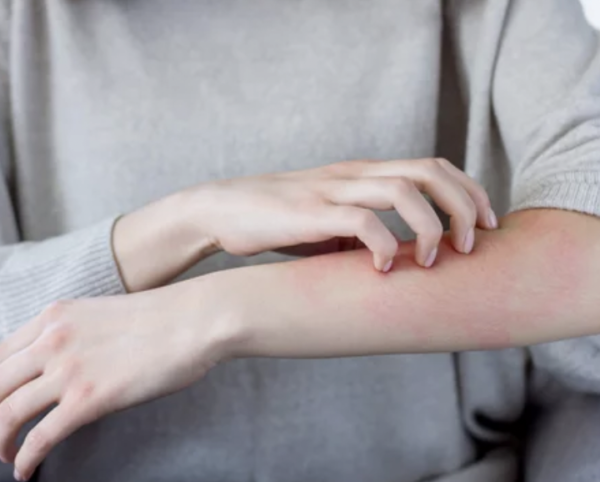
Bacterial Metabolites: A Link between Gut Microbiota and Dermatological Diseases
Would you like to know one of the most important factors affecting the health of your largest organ?
Gut microbiota plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s immune system; therefore, imbalances in it can lead to dermatological diseases. This article highlights how bacterial metabolites produced by the gut microbiota can impact skin health and the role of short-chain fatty acids and their anti-inflammatory properties in this relation. They also suggest that understanding the link between gut microbiota and skin health could lead to new approaches for preventing and treating dermatological diseases.